The Future of Eco-Friendly Technology: A-Frame BTEX Systems Explained!

As the world grapples with the pressing need to address environmental concerns, the role of eco-friendly technologies becomes increasingly significant. Among the myriad solutions being developed, A-Frame BTEX systems stand out as a promising innovation in the realm of environmental engineering. These systems are designed to tackle one of the most challenging pollutants: BTEX compounds. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of A-Frame BTEX systems, their significance, and their potential to revolutionize the way we manage environmental pollution.
Understanding BTEX Compounds
BTEX stands for Benzene, Toluene, Ethylbenzene, and Xylene, a group of volatile organic compounds commonly found in petroleum products. These compounds are prevalent in various industrial processes, including the production of plastics, resins, and synthetic fibers. Despite their widespread use, BTEX compounds pose significant environmental and health risks. They are known to contribute to air and water pollution and have been linked to serious health issues, including respiratory problems, neurological damage, and cancer.
The Need for BTEX Mitigation
The pervasive nature of BTEX compounds in industrial emissions necessitates effective mitigation strategies. Traditional methods of dealing with BTEX pollution, such as activated carbon adsorption and catalytic oxidation, have limitations in terms of efficiency, cost, and environmental impact. This has led to the exploration of more innovative and sustainable approaches, paving the way for technologies like the A-Frame BTEX system.
What is an A-Frame BTEX System?
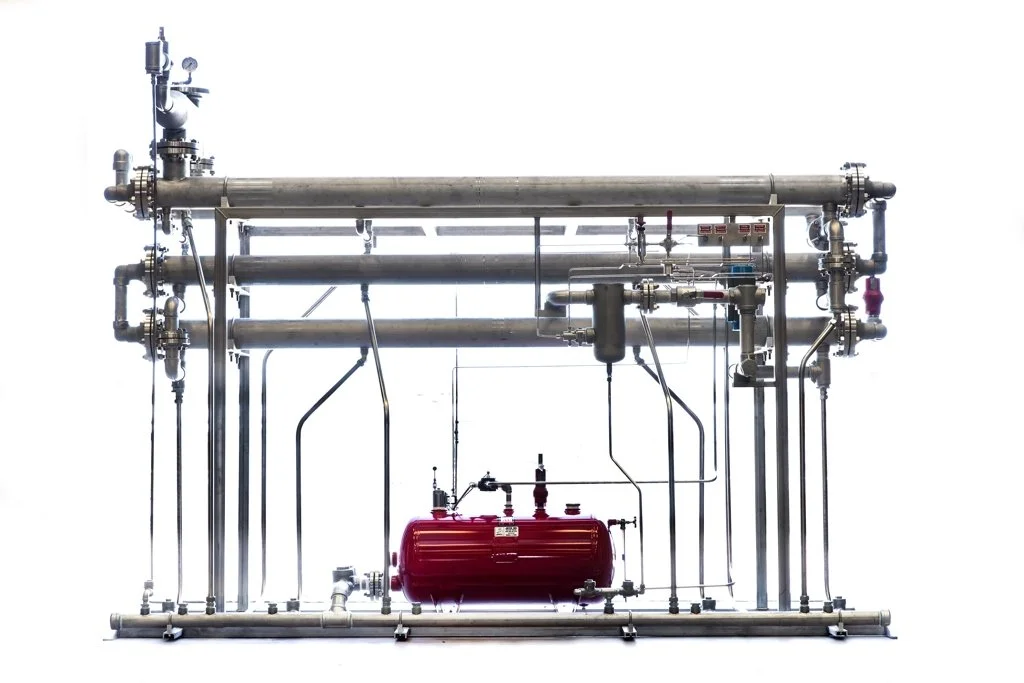
An A-Frame BTEX system is a specialized type of air pollution control technology designed to capture and neutralize BTEX compounds from industrial emissions. The system is named after its distinctive A-frame structure, which maximizes the surface area for pollutant capture and enhances the efficiency of the purification process.
Key Components of an A-Frame BTEX System
- A-Frame Structure: The hallmark of the system, the A-frame design, provides a large surface area for the adsorption of BTEX compounds. This structure allows for a more compact and efficient setup compared to traditional flat-bed designs.
- Adsorption Media: Typically, the A-Frame BTEX system uses advanced adsorption materials such as activated carbon, zeolites, or specially designed polymeric adsorbents. These materials have high affinity for BTEX compounds and can effectively capture them from the air stream.
- Regeneration Mechanism: One of the critical aspects of the system is the ability to regenerate the adsorption media. This is usually achieved through thermal or vacuum regeneration, where the adsorbed BTEX compounds are desorbed from the media, allowing it to be reused.
- Emission Control: The system incorporates various emission control technologies to ensure that the desorbed BTEX compounds are either destroyed or converted into less harmful substances. This can include catalytic oxidation, where the BTEX compounds are oxidized into carbon dioxide and water.
How A-Frame BTEX Systems Work
The operation of an A-Frame BTEX system can be broken down into several stages:
- Capture: Industrial emissions containing BTEX compounds are directed through the A-frame structure, where the adsorption media capture the pollutants.
- Adsorption: The BTEX compounds adhere to the surface of the adsorption media, effectively removing them from the air stream.
- Regeneration: Once the adsorption media reaches its capacity, the system initiates a regeneration process. This typically involves heating the media to release the captured BTEX compounds.
- Destruction: The released BTEX compounds are then treated using catalytic oxidation or other methods to neutralize them.
- Recycling: The regenerated adsorption media is ready for another cycle of BTEX capture, making the system highly efficient and sustainable.
Advantages of A-Frame BTEX Systems
- High Efficiency: The A-frame design provides a large surface area for adsorption, enhancing the system's ability to capture BTEX compounds efficiently.
- Compact Design: The unique structure allows for a more compact setup, making it suitable for facilities with limited space.
- Sustainability: The regeneration mechanism reduces the need for frequent replacement of adsorption media, minimizing waste and operational costs.
- Cost-Effective: Over time, the ability to regenerate the adsorption media and the high efficiency of pollutant capture can lead to significant cost savings.
- Environmental Impact: By effectively capturing and neutralizing BTEX compounds, the system helps reduce air and water pollution, contributing to a cleaner environment.
Applications of A-Frame BTEX Systems
A-Frame BTEX systems have a wide range of applications across various industries:
- Petrochemical Plants: These facilities are major sources of BTEX emissions. The A-Frame BTEX system can be integrated into their emission control strategies to reduce the release of harmful pollutants.
- Refineries: Oil refineries generate significant amounts of BTEX compounds. Implementing A-Frame BTEX systems can help mitigate their environmental impact.
- Chemical Manufacturing: Industries involved in the production of chemicals, resins, and plastics can benefit from the efficient BTEX capture capabilities of these systems.
- Environmental Remediation: A-Frame BTEX systems can also be used in environmental remediation projects to clean up contaminated sites and prevent further pollution.
Challenges and Future Prospects
While A-Frame BTEX systems offer numerous benefits, there are challenges that need to be addressed to ensure their widespread adoption:
- Initial Costs: The upfront costs of installing A-Frame BTEX systems can be high, which may deter some industries from adopting the technology.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance is required to ensure the system operates at peak efficiency. This includes periodic checks and regeneration of the adsorption media.
- Technological Advancements: Continuous research and development are necessary to improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of these systems.
Despite these challenges, the future prospects for A-Frame BTEX systems are promising. With increasing regulatory pressure to reduce industrial emissions and growing awareness of environmental issues, the demand for effective pollution control technologies is set to rise. Innovations in materials science and engineering will likely lead to further improvements in the performance and affordability of A-Frame BTEX systems.
Conclusion
A-Frame BTEX systems represent a significant advancement in the field of eco-friendly technology. By providing an efficient and sustainable solution for capturing and neutralizing BTEX compounds, these systems hold the potential to mitigate one of the most challenging aspects of industrial pollution. As industries continue to seek ways to reduce their environmental footprint, the adoption of A-Frame BTEX elimination systems could play a crucial role in achieving cleaner and healthier surroundings. The future of eco-friendly technology is indeed bright, and A-Frame BTEX systems are poised to be at the forefront of this transformative journey.
